Many people with diabetes don’t realize it can lead to a serious eye disease called diabetic retinopathy. This condition damages the light-sensitive area at the back of the eye (the retina) and can cause vision loss over time.
Knowing the different stages of diabetic retinopathy is crucial for people with diabetes. There are 4 stages: mild nonproliferative retinopathy, moderate nonproliferative retinopathy, severe nonproliferative retinopathy, and proliferative retinopathy.
If you have diabetes, learning about diabetic retinopathy can help you recognize symptoms early and talk to your eye doctor to proactively manage your ocular health.
Diabetes & Your Eyes
Diabetes and eye health are closely linked. High blood sugar, if uncontrolled, can damage blood vessels throughout your body, including the tiny ones in your eyes. This damage is called diabetic retinopathy. It can cause swelling (macular edema) and other problems that affect your vision. The earlier you understand this risk, the sooner you can take steps to protect your eyesight.
What Is Diabetic Retinopathy?
In simple terms, diabetic retinopathy is a diabetes complication that affects the eyes. It’s caused by damage to the blood vessels of the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye (retina). At first, you might not notice any changes to your vision. But, over time, diabetic retinopathy can get worse and cause vision loss.
Diabetic retinopathy usually affects both eyes.
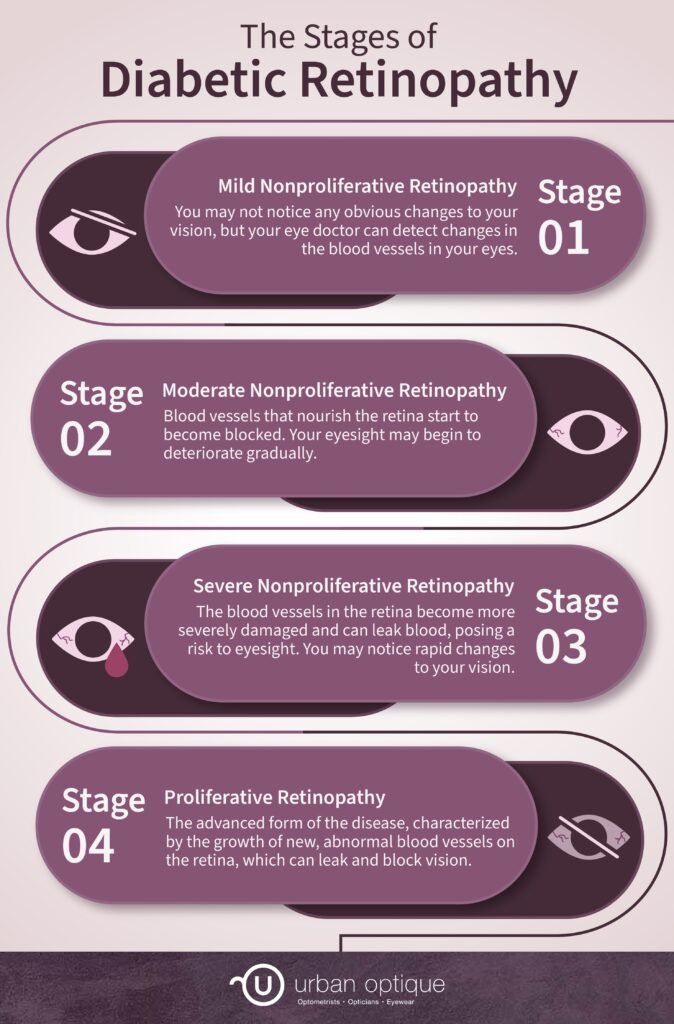
Stage 1: Mild Nonproliferative Retinopathy
At first, diabetic retinopathy may not cause any vision problems. But an eye doctor can see tiny bulges (like balloons) in the blood vessels of your retina during an exam. These bulges, called microaneurysms, usually don’t need treatment, but they’re a sign to keep a close eye on your eye health.
The Importance of Early Detection
Even though early diabetic retinopathy might not affect your vision yet, it’s a cue to manage your diabetes better. Early detection allows your eye doctor to track the disease and prevent it from getting worse.
Stage 2: Moderate Nonproliferative Retinopathy
In this stage, blood vessels that nourish the retina start to become blocked, leading to reduced blood flow and cell death in nerves in the retina. Your eyesight may begin to deteriorate, but the changes are usually gradual.
At this stage, meticulous diabetes care and regular eye checkups are crucial, as the thinning of the nerves can lead to more severe complications.
Stage 3: Severe Nonproliferative Retinopathy
At this stage, the blood vessels in the retina become more severely damaged, causing them to become more blocked. This can starve the retina of necessary blood supply, leading to the growth of new, abnormal blood vessels. These new blood vessels are fragile and can leak blood, posing a real risk to eyesight.
Impacts & Adjustments
This development can mean more rapid changes to your vision, but it also signifies the need for medical intervention. Your visual acuity may decline noticeably, and symptoms like floaters and dark spots in your vision field can indicate the need for prompt action.
Stage 4: Proliferative Retinopathy
Proliferative retinopathy is the advanced form of the disease, characterized by the growth of new, abnormal blood vessels on the retina’s surface, which can leak into the eye’s clear, jelly-like substance (vitreous), blocking vision. This can lead to further complications such as retinal detachment or glaucoma, both of which require immediate attention.
Treatment & Management
Fortunately, several treatment options are available, including laser surgery to shrink the abnormal blood vessels or injections into the vitreous to prevent new blood vessels from forming.
Managing vision at this stage is critical and often includes ongoing treatments in coordination with overall diabetes healthcare.
How to Protect Your Vision
Regular eye exams should be a primary part of your healthcare routine, as they can detect early signs of diabetic retinopathy and enable swift intervention to avert further damage.
The Role of Diet & Lifestyle
A healthy diet and active lifestyle are your allies in managing diabetes and, by extension, diabetic retinopathy. Eat lots of colourful fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and stay active to keep weight and blood sugar levels within a healthy range.
Medical Intervention
When necessary, don’t hesitate to seek medical care for diabetic retinopathy. Treatments alongside other strategies employed in later stages of the disease can help manage the condition.
Spot Diabetic Eye Disease Early
Early detection and proactive management of diabetes can safeguard your overall health and are crucial in preserving your vision. Managing diabetes and its complications is more than medication—it’s a proactive, daily effort toward wellness that can be sight-saving.
Visit us at Urban Optique for your next comprehensive eye exam, and let us help you put your ocular health first.
















